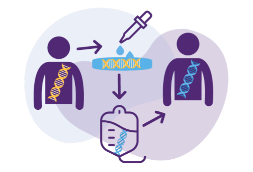
What is gene therapy?
The goal of gene therapy is to target
These changes affect how the proteins that cause disease function.

FIND
Gene therapy alters a specific gene.
CHANGE
A gene can be added, turned on, or turned off inside the cell.
MODIFY
The newly added or altered genes change the proteins.
CREATE
The new proteins may work in place of the faulty proteins.
Understanding the differences between gene addition and gene editing
When we learned about genetics and mutations, we talked about how your genes are like your body’s instruction manual. When there is a mistake, the body doesn’t work the way it’s supposed to, and a genetic disease results.
Gene therapy works in different ways. To get a better idea, we have to think about different problems you may find in the instruction manual.
Instruction manuals can contain incorrect information. For example, if 1 word is incorrect, it can change the meaning of a sentence. Let’s explore 2 ways you could correct the instructions:
You’ve learned about the types and delivery methods of gene therapy. Next, let’s look at the research and how it’s affecting genetic diseases in the real world.
Learn more
Sign up to receive the latest resources direct to your inbox.